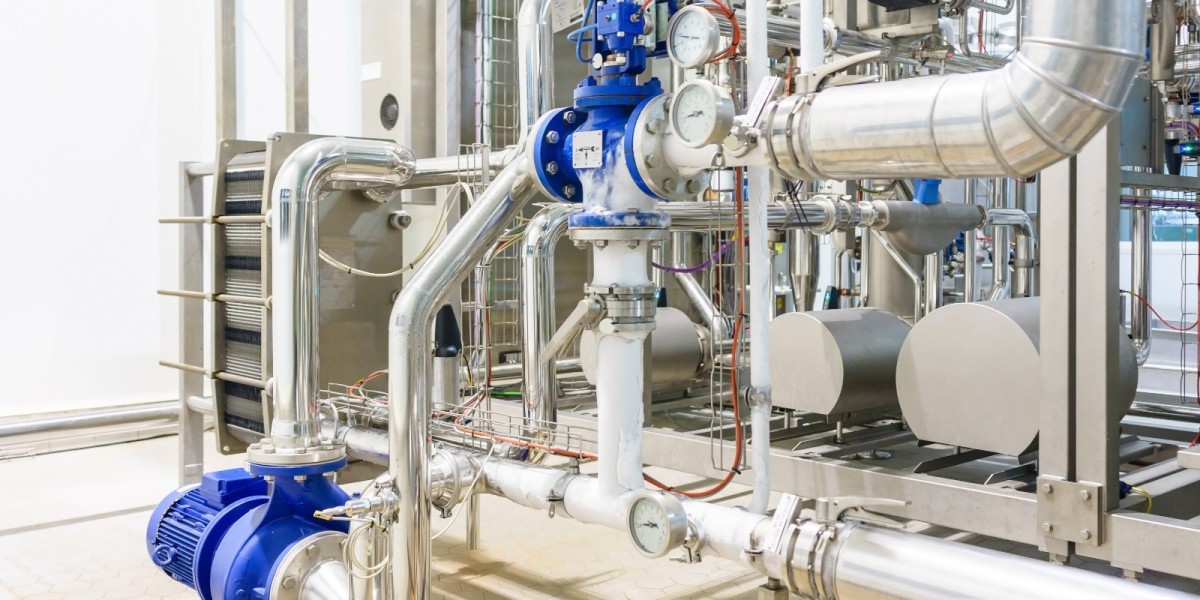
Valves are essential components in manufacturing and process industries, playing a critical role in controlling the flow of liquids, gases, and slurries. From regulating pressures to isolating systems during maintenance, reliable valves ensure the smooth operation of industrial processes, minimize downtime, and enhance safety. In manufacturing and process industries where efficiency, precision, and durability are paramount, selecting the right valve solution is a key factor in achieving operational excellence.
This article explores the significance of reliable valve solutions, their types, applications, selection criteria, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of industrial valve technology.
Importance of Reliable Valves in Manufacturing and Process Industries
In industrial processes, valves must endure harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, extreme pressures, and exposure to corrosive substances. A reliable valve system minimizes leakage, reduces the risk of system failure, and optimizes resource utilization.
Key Benefits of Reliable Valve Solutions:
- Operational Efficiency: Ensures smooth flow and reduces energy consumption.
- Safety: Prevents accidents caused by leaks or overpressure.
- Durability: Minimizes maintenance costs and extends the life of equipment.
- Environmental Compliance: Helps industries meet emission and waste management regulations.
Types of Valves in Manufacturing and Process Industries
Various types of valves are used in industrial processes, each tailored to specific functions and applications.
1. Gate Valves
- Function: Provide on/off control with minimal pressure drop.
- Advantages: Simple design, durable, and effective for full-flow applications.
- Applications: Oil refineries, chemical plants, and water treatment facilities.
2. Globe Valves
- Function: Precise flow control and throttling.
- Advantages: Excellent sealing capabilities and reliable performance.
- Applications: Steam systems, fuel processing, and cooling water lines.
3. Ball Valves
- Function: Quick shutoff and flow control.
- Advantages: Compact, durable, and low-maintenance.
- Applications: Chemical handling, petrochemical processes, and natural gas pipelines.
4. Butterfly Valves
- Function: Regulate flow with a compact design.
- Advantages: Lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for large-diameter pipelines.
- Applications: HVAC systems, water distribution, and food processing.
5. Check Valves
- Function: Prevent backflow to protect equipment.
- Advantages: Automatic operation and low-pressure drop.
- Applications: Pumps, compressors, and pipeline systems.
6. Diaphragm Valves
- Function: Ideal for corrosive and viscous media.
- Advantages: Hygienic design with minimal dead space.
- Applications: Pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and wastewater treatment.
7. Pressure-Relief Valves
- Function: Release excess pressure to protect systems from overloading.
- Advantages: Critical for safety and compliance.
- Applications: Chemical reactors, boilers, and storage tanks.
8. Control Valves
- Function: Automatically adjust flow, pressure, or temperature.
- Advantages: Highly precise and customizable.
- Applications: Power plants, oil and gas pipelines, and process control systems.
Applications of Valves in Manufacturing and Process Industries
Valves are integral to a wide range of industrial processes, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
1. Oil and Gas Industry
- Control flow and pressure in drilling, refining, and transportation processes.
- Handle high pressures and corrosive substances like hydrogen sulfide.
2. Chemical Processing
- Manage the flow of aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents.
- Ensure safety in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
3. Water Treatment
- Regulate water flow in filtration, desalination, and wastewater management systems.
- Prevent contamination with hygienic valve designs.
4. Power Generation
- Control steam, water, and fuel in thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric power plants.
- Maintain precise flow rates to optimize energy efficiency.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Ensure sterility and precision in drug manufacturing processes.
- Handle sensitive materials with hygienic and corrosion-resistant valves.
6. Food and Beverage Production
- Facilitate clean and efficient handling of liquids and gases.
- Comply with sanitary standards to ensure product safety.
Key Features of Reliable Valve Solutions
A reliable valve solution must meet the unique demands of manufacturing and process industries.
1. Material Durability
- Materials like stainless steel, cast iron, and exotic alloys resist wear, corrosion, and extreme conditions.
2. Tight Sealing
- Prevents leaks and enhances safety, especially in hazardous environments.
3. Automation Compatibility
- Integration with actuators and sensors for advanced control and monitoring.
4. Ease of Maintenance
- Modular designs simplify repairs and reduce downtime.
5. Compliance
- Adherence to standards like API, ISO, and ASME ensures safety and quality.
Selection Criteria for Valves
Choosing the right valve is critical for ensuring process efficiency and safety.
Key Considerations:
- Media Type: Compatibility with the fluid or gas being handled.
- Pressure and Temperature: Ability to withstand operating conditions.
- Flow Requirements: Match valve design to desired flow rates and control.
- Environment: Resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and environmental factors.
- Automation Needs: Integration with existing control systems.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Reliable valves require regular maintenance to prevent failures and extend their lifespan.
Maintenance Tips:
- Inspect seals, gaskets, and actuators periodically.
- Lubricate moving parts with suitable lubricants.
- Clean valves to prevent clogging, especially in slurry systems.
- Replace worn-out components promptly to avoid system failures.
Common Issues and Solutions:
- Leakage: Check and replace damaged seals or seats.
- Corrosion: Use corrosion-resistant materials or apply protective coatings.
- Sticking Valves: Regular cleaning and lubrication can prevent sticking.
- Pressure Drops: Ensure proper valve sizing and design for the application.
Trends in Valve Technology
The evolution of valve technology is driving efficiency and innovation in manufacturing and process industries.
1. Smart Valves
- Equipped with sensors for real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Enable predictive maintenance to reduce downtime.
2. Eco-Friendly Designs
- Focus on minimizing leaks and emissions.
- Use sustainable materials and manufacturing practices.
3. High-Performance Materials
- Advanced alloys and composites improve resistance to extreme conditions.
4. Automation and IoT Integration
- Valves with actuators and IoT connectivity enhance process control.
Conclusion
Reliable valve solutions are the backbone of manufacturing and process industries, ensuring efficiency, safety, and compliance. By selecting the right valve type, adhering to maintenance best practices, and leveraging emerging technologies, businesses can optimize their operations and stay ahead in competitive markets. As industries embrace automation and sustainability, the role of innovative valve technologies will continue to grow, driving excellence across all sectors.